Relative expression software tool (REST) for group-wise comparison and statistical analysis of relative expression results in real-time PCR.
Real-time reverse transcription adopted by polymerase chain response (RT-PCR) is essentially the most appropriate technique for the detection and quantification of mRNA. It affords excessive sensitivity, good reproducibility and a large quantification vary.
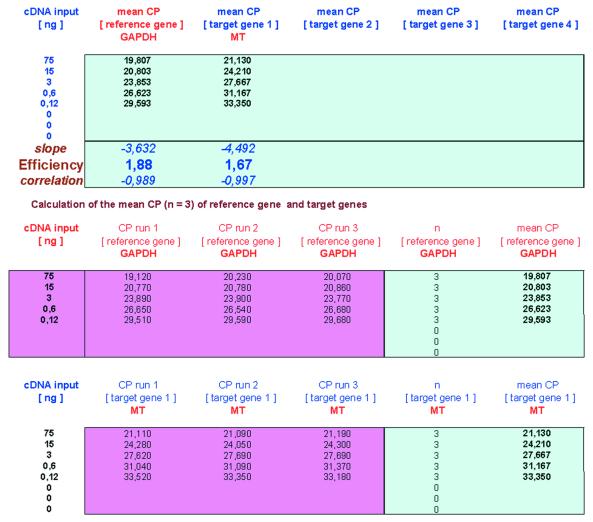
Today, relative expression is more and more used, the place the expression of a goal gene is standardised by a non-regulated reference gene. Several mathematical algorithms have been developed to compute an expression ratio, based mostly on real-time PCR effectivity and the crossing level deviation of an unknown pattern versus a management.
But all printed equations and accessible fashions for the calculation of relative expression ratio permit solely for the willpower of a single transcription distinction between one management and one pattern.
Therefore a brand new software tool was established, named REST (relative expression software tool), which compares two teams, with as much as 16 information factors in a pattern and 16 in a management group, for reference and as much as 4 goal genes.
The mathematical mannequin used is predicated on the PCR efficiencies and the imply crossing level deviation between the pattern and management group. Subsequently, the expression ratio results of the 4 investigated transcripts are examined for significance by a randomisation check. Herein, improvement and software of REST is defined and the usefulness of relative expression in real-time PCR utilizing REST is mentioned.
New heterologous modules for classical or PCR-based gene disruptions in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.
We have constructed and examined a dominant resistance module, for choice of S. cerevisiae transformants, which totally consists of heterologous DNA. This kanMX module accommodates the identified kanr open reading-frame of the E. coli transposon Tn903 fused to transcriptional and translational management sequences of the TEF gene of the filamentous fungus Ashbya gossypii. This hybrid module permits environment friendly choice of transformants resistant towards geneticin (G418).
We additionally constructed a lacZMT reporter module in which the open reading-frame of the E. coli lacZ gene (missing the primary 9 codons) is fused at its 3′ finish to the S. cerevisiae ADH1 terminator.
KanMX and the lacZMT module, or each modules collectively, had been cloned in the middle of a brand new a number of cloning sequence comprising 18 distinctive restriction websites flanked by Not I websites. Using the double module for constructions of in-frame substitutions of genes, just one transformation experiment is important to check the exercise of the promotor and to look for phenotypes because of inactivation of this gene.
To permit for repeated use of the G418 choice some kanMX modules are flanked by 470 bp direct repeats, selling in vivo excision with frequencies of 10(-3)-10(-4). The 1.Four kb kanMX module was additionally proven to be very helpful for PCR based mostly gene disruptions.
In an experiment in which a gene disruption was accomplished with DNA molecules carrying PCR-added terminal sequences of solely 35 bases homology to every goal website, all twelve examined geneticin-resistant colonies carried the appropriately built-in kanMX module.
